Ground Lamb Vs Ground Beef Nutrition

vs

Summary
Lamb is higher in calories, fats, including saturated, polyunsaturated fatty and cholesterol, essential amino acids, and most vitamins. At the same time, beef is richer in protein due to more non-essential amino acids, fe, zinc, and vitamin B6.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Nomenclature
- Appearance
- Taste and Apply
- Cost
- Varieties
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients and Calories
- Calories
- Poly peptide
- Fats and Cholesterol
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Glycemic Index
- Acidity
- Weight Loss & Diets
- Health Impact
- Health Benefits
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes
- Downsides and Risks
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Bans and Faith
- Bear upon on the Environs
- References
Introduction
People often cull meat based on its subjective qualities, such as gustatory modality and texture. However, different types of meat can vary with their nutrition and their touch on on health. In this article, nosotros will discuss the differences and similarities between lamb or mutton and beef based on scientifically proven information.
Nomenclature
The master difference between lamb or mutton and beef is naturally the fauna they come from.
Lamb, mutton, and hogget are all names for domestic sheep meat. However, these terms are non interchangeable. Mutton or hogget is the meat of fully grown sheep, normally two and three years of age, respectively, while lamb is the meat of a sheep younger than the age of one.
Beef is the meat of older cattle: domesticated cows or bulls. The meat of young cattle is called veal. To run into a consummate comparison of veal and lamb or mutton, you can visit this page.
Lamb and beef are both classified as red meat. Compared to white meat, red meat is darker in colour and richer in myoglobin, and therefore heme iron.
Advent
Lamb and beefiness meat can be very difficult to tell apart based on appearance lone. Beef and lamb are dark in color, both beingness types of red meat. Withal, when comparison the ii, beef can appear to exist darker due to a higher iron and myoglobin content.
Both beef and lamb have white stripes of intermuscular fat chosen marbling. The amount of marbling in the meat depends on the cut.
Taste and Utilize
Mutton and beef are like in taste. This gustation of cherry meat is described as umami. Depending on the fatty content, information technology can likewise be buttery and soft or dry out and firm.
Compared to mutton and beef, lamb is said to take a more tender texture and a more than delicate flavor.
Beef is used in cultures all over the world, while lamb and mutton are more common in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine.
Beef and lamb are oftentimes used in their ground form, particularly in burgers. Beef burgers are a lot more popular than lamb burgers.
Toll
On average, in the The states market place, beefiness tends to be a piddling cheaper past about 0.3$.
Varieties
The nutritional and culinary qualities of meat tin can differ based on the type of meat. Meat tin can exist classified based on the cutting or how the animal was raised.
Cuts of beefiness include the chuck (shoulder), the brisket and shank (breast), the rib, the sirloin (hip), the short loin, the short plate, the fleck, and the round.
Similarly, depending on the cutting, y'all can find the following varieties of lamb or mutton: the square cut shoulder, the rack or rib, the loin, the leg, the neck, the breast, the shanks, and the flank.
How the animal has been raised also has a part in the characteristics of the meat. Depending on the conditions in which the cows have been kept, beef tin can be formula-fed, also known as milk-fed or white, not-formula fed, also known as ruddy, pasture-raised, or costless-raised. Beef can also be grass-fed or organic.
All red meat can be processed or unprocessed. Meat undergoes processing to extend its shelf life, every bit well as to ameliorate its taste, color, and appearance. These processing methods include curing, smoking, salting, drying, or adding preservatives and colorings. Some examples of processed red meat are ham, sausages, salami, and pepperoni.
Diet
The nutrition of meat greatly varies depending on the cut and fat content.
The nutritional values below are presented for cooked domestic lamb, a composite of trimmed retail cuts, trimmed to ¼ inch fat, and baked ground beef with 15% fat and 85% lean meat.
Macronutrients and Calories
Overall, lamb is denser in nutrients, as it contains just around 54% water and 46% nutrients, while beefiness consists of 58% water.
As with virtually meat, the average serving size for both lamb and beef is 3oz, equal to 85g.
Calories
Lamb and beefiness are both loftier-calorie foods. Nevertheless, lamb provides more than energy between the two, containing 294 calories per 100g serving, while the same serving size of beef has 250 calories.
Notwithstanding, the calorie content of meat can significantly alter with a different cut or cooking method. When comparison only lean cuts of roasted beefiness tenderloin or loin with a completely lean cut of fast fried lamb tenderloin, we find that the lamb tin be slightly lower in calories. Lean lamb tenderloin contains 155 calories, while lean beef tenderloin provides 168 calories (1, 2).
Poly peptide
While being less dense in nutrients, beef is withal richer in poly peptide. A 100g serving of beef provides 25.93g of protein. At the same fourth dimension, the aforementioned serving size of lamb contains 24.52g of poly peptide.
Despite being lower in protein overall, lamb is richer in all of the essential amino acids. Therefore, the protein institute in lamb is of higher quality.
Lamb is peculiarly richer in tryptophan, containing over three times more than than beef.
Of the not-essential amino acids, lamb is besides richer in aspartic and glutamic acids.
Fats and Cholesterol
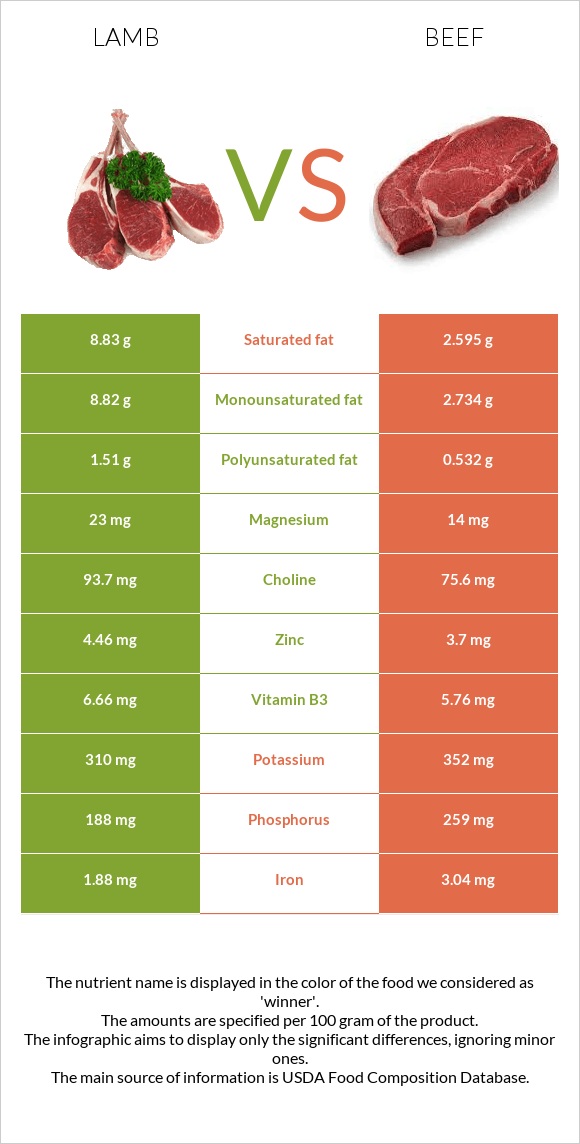
Between these two cuts of meat, lamb is notably richer in fats. The same 100g serving size of cooked lamb contains well-nigh 21g of fats, while cooked beefiness provides 15.4g of fats.
Naturally, lamb is higher in all types of fat: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. Nonetheless, while lamb meat is simply 1.5 times higher in saturated fatty than beef, it is over 3 times richer in polyunsaturated fat acids.
Overall the fat acrid limerick in beef is every bit follows: 45% saturated fats, 51% monounsaturated fats, and 4% polyunsaturated fats. Lamb, on the other hand, consists of 46% saturated fats, 46% monounsaturated fats, and 8% polyunsaturated fats.
Unsurprisingly, lamb is also slightly higher in cholesterol. The same 100g serving size of lamb contains 97mg of cholesterol, while beefiness contains 88mg.
Carbohydrates
Like most meat, both beef and lamb comprise no notable corporeality of carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Overall, lamb and mutton tend to exist more abundant in vitamins. Lamb and mutton contain 2 times more folate, vitamin B1, and nearly four times more than vitamin K. Lamb or mutton is also richer in vitamin B2, vitamin B3, and vitamin E.
Beefiness, on the other mitt, provides 3 times more than vitamin B6.
Lamb or mutton contains vitamin D, which beef lacks completely. At the same time, vitamin A can be constitute in beef only not in lamb.
The 2 types of meat are almost equal in the independent amounts of vitamin B12 and vitamin B5, with beef being merely a little richer in vitamin B12.
Lamb, mutton, and beefiness are all absent in vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs tin exist covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
viii
:
three
![]()
Contains more Vitamin East +xvi.7%
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +117.4%
Contains more than Vitamin B2 +42%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +23.viii%
Contains more Folate +100%
Contains more Vitamin K +283.3%
Contains more Vitamin A +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +193.8%
Equal in Vitamin B5 - 0.658
Equal in Vitamin B12 - 2.64
Contains more Vitamin East +16.7%
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +117.4%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +42%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +23.eight%
Contains more Folate +100%
Contains more Vitamin K +283.3%
Contains more than Vitamin A +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +193.8%
Equal in Vitamin B5 - 0.658
Equal in Vitamin B12 - 2.64
Minerals
Meat can be an important source of almost all the minerals needed in a diet. While beef and lamb are not cardinally dissimilar in their mineral compositions, there are some differences.
Beef is a improve source of atomic number 26 and zinc. Beef is besides slightly higher in potassium, phosphorus, and calcium.
On the other hand, lamb contains i.four times more than copper, as well as relatively college levels of selenium, magnesium, manganese, and choline.
Lamb and beefiness contain equal amounts of sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals by which one or the other nutrient is richer. The "coverage" chart below prove how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
two
:
five
![]()
Contains more Copper +40%
Contains more than Iron +38.3%
Contains more Zinc +41.5%
Equal in Calcium - 18
Equal in Magnesium - 21
Equal in Phosphorus - 198
Equal in Potassium - 318
Equal in Sodium - 72
Contains more Copper +40%
Contains more Iron +38.three%
Contains more than Zinc +41.five%
Equal in Calcium - 18
Equal in Magnesium - 21
Equal in Phosphorus - 198
Equal in Potassium - 318
Equal in Sodium - 72
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of both lamb and beef is considered to be 0 due to the absenteeism of carbohydrates. You tin learn more virtually the glycemic index of foods with low or no carbohydrates.
Acidity
The pH of meat changes depending on its freshness and the conditions in which it has been kept.
The acceptable range of the pH value for beef falls between five.3 to v.7. As the pH value of beef reaches 6.5, it starts to decompose (3). This ways that beef has an acidic pH value.
The pH value of lamb can vary between 5.7 to 6.05 (4). Evidently, the pH of lamb tends to be more than acidic than that of beefiness.
Another way of measuring the acidity of a sure food is by looking at its potential renal acid load or PRAL value, which shows how much acid or base information technology produces.
The PRAL values of lamb and beefiness are eleven.half dozen and 12.half-dozen, respectively. This demonstrates how beef is slightly more than acid-producing within the organism.
Weight Loss & Diets
Lamb, mutton, and beef are all high-calorie foods. However, this does not necessarily exclude these foods from weight loss diets, as they are high in protein just very low in carbohydrates.
Between these ii types of meat, beef is the better selection for low-calorie and low-fat diets. Both lamb and beef fit well into low carb and low glycemic index diets.
Inquiry has found a correlation between high meat intake and increased risk of weight gain and obesity (v, half-dozen). Notwithstanding, this take a chance is higher with processed and fatty meats, as opposed to unprocessed and lean meats (7).
Red meat, including both lamb and beef, is a major role of the keto and Atkins diets.
A Paleo nutrition allows the consumption of unprocessed lamb, mutton, and beef, but non candy meat.
Consumption of lamb and beef inside limits tin can also be a part of a Mediterranean diet.
Health Impact
Scarlet meat and its effects on wellness have been at the center of attending for many researchers for several decades. Even so, while some things are certain, science is nonetheless inconclusive well-nigh other areas. In this section, we volition hash out the most popular studies examining red meat, including lamb and beefiness, and its impact on health.
Health Benefits
Overall, lean and unprocessed meat has a more benign affect on health than fatty and processed meats. While lamb and beef have like fatty compositions, lamb tends to have a more favorable fatty contour between the two.
Cardiovascular Health
A healthy diet, depression in saturated fats and high in lean beefiness, has been researched to lead to favorable effects on cardiovascular disease due to decreased levels of full cholesterol and depression-density lipoproteins (8).
A diet low in calories merely high in protein from lean red meat can also improve chance markers of cardiovascular disease and type two diabetes (9).
S African lamb, in particular, has been studied to be a good source of poly peptide, with its moderate intake potentially decreasing levels of homocysteine in the claret (10).
Diabetes
Equally mentioned above, a depression-calorie nutrition loftier in lean red meat may have a beneficial effect on the run a risk markers of blazon 2 diabetes mellitus (ix).
Downsides and Risks
The possible mechanisms of action for the adverse effects of scarlet meat include inflammation, oxidative stress, and negative effects on the liver, pancreas, and fat cells due to high levels of heme iron, saturated fats, branched amino acids, and other compounds. (11).
Dissimilar unprocessed red meat, processed red meat undergoes various treatments to extend its shelf life. Candy crimson meat may contain college levels of sodium and nitrates, equally well as additives and contaminants. These contaminants can accept various harmful effects on wellness (11).
Cardiovascular Health
Diverse studies have shown a correlation between the consumption of both candy and unprocessed reddish meat and an increased take chances of stroke, coronary middle disease, and potentially even heart failure (xi).
Due to the heme fe content, loftier consumption of red meat has as well been associated with higher blood force per unit area (12).
Diabetes
A considerable number of studies have consistently shown that a diet rich in blood-red, and especially processed, meat is associated with an increased take a chance of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The risk of type two diabetes can increase depending on the grooming method of the meat. Research suggests that certain grooming methods, in particular the utilise of high heat cooking methods, such equally broiling, barbecuing, or grilling and roasting, increment the risk of type 2 diabetes (13).
Cancer
The do of cooking meat at high temperatures, such as pan-frying and barbecuing, may lead to the production of heterocyclic amines, which are thought to increase cancer run a risk in humans (11).
Grilled or barbecued meats may also comprise high levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which promote the development of cancer and Dna damage (14).
Research has found that a high intake of both processed and unprocessed scarlet meat may increase the take a chance of esophageal, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers (11).
Bans and Religion
Beefiness is considered to be a respected creature of God in Hinduism. Due to this reason, at that place are laws in Bharat prohibiting the slaughtering of cows which vary past state. Slaughtering a cow in India is punishable by police, with a jail sentence from 6 months upwardly to 10 years, depending on the country.
Consumption of sheep meat is not prohibited in any major religion of the world.
Impact on the Environment
Over the concluding few decades, public business has grown over the impact of mass red meat production on the surroundings and climate change. Red meat product leads to large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions, fossil energy, and water use, amidst other things.
The product of lamb has a larger impact on greenhouse gas emissions when compared to beefiness product.
The greenhouse gas emission, expressed every bit CO2 equivalents, for the product of 1kg of lamb is l, while the same number for beefiness is 30 (15).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172622/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/746758/nutrients
- The issue of pH on beef eating quality
- pH values of the fresh different meat types during chilled storage at ii • C
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/manufactures/PMC2697260/
- https://bmcnutr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40795-016-0063-9
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/108/1/33/5036105
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/manufactures/PMC3238465/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31771921/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4213744/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joim.12543
- https://www.bmj.com/content/337/bmj.a258
- How Meat Is Cooked May Affect Risk of Type two Diabetes
- https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/235
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22964113/
Infographic
Which food is preferable for your diet?
![]()
![]()
is better in case of low diet
 |  | |
| Low Fats diet | | |
| Low Carbs diet | Equal | |
| Low Calories diet | | |
| Low glycemic index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamin and Mineral Summary Scores
The summary score is calculated by summing up the daily values contained in 300 grams of the product. Evidently the more than the food fulfills homo daily needs, the more the summary score is.
Vitamin Summary Score
52
![]()
52
![]()
Mineral Summary Score
46
![]()
55
![]()
Macronutrients Comparing
Macronutrient comparison charts compare the amount of poly peptide, total fats, and full carbohydrates in 300 grams of the food. The displayed values prove how much of the daily needs can exist covered past 300 grams of nutrient.
Protein
147%
![]()
156%
![]()
Carbohydrates
0%
![]()
0%
![]()
Fats
97%
![]()
71%
![]()
Comparing summary
Which food is richer in vitamins?
![]()
Lamb and mutton is relatively richer in vitamins
Which food is lower in Cholesterol?
![]()
Beef is lower in Cholesterol (difference - 9mg)
Which food is lower in Saturated Fat?
![]()
Beefiness is lower in Saturated Fat (difference - 2.935g)
Which food is cheaper?
![]()
Beef is cheaper (difference - $0.3)
Which food is richer in minerals?
![]()
Beef is relatively richer in minerals
Which food contains less Sugar?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Sugar (0 g)
Which food contains less Sodium?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Sodium (72 mg)
Which food is lower in glycemic alphabetize?
?
The foods have equal glycemic indexes (0)
molinaheratat1982.blogspot.com
Source: https://foodstruct.com/compare/lamb-vs-beef

0 Response to "Ground Lamb Vs Ground Beef Nutrition"
Post a Comment